Learn More About Thermoforming
Thermoforming is the process by which three dimensional plastic parts are shaped from a softened
thermoplastic sheet. The process involves heating a plastic sheet to a temperature range where it is
soft, and then stretching it against a cool mold surface. When the sheet has cooled to the point where
it retains the shape of the mold, the sheet is removed from the mold and excess plastic trimmed from the
part.
The first step in making a vacuum formed part is fabricating the forming mold or tool. Vacuum forming
molds can be made from a variety of materials ranging from wood to steel and can be single cavity or
multi cavity. Once produced, the tool needs to be vented so that all inside corners have a way to
evacuate air once the softened sheet is pulled over the mold. Proper venting is critical to ensure that
the plastic sheet is pulled completely against the tool.
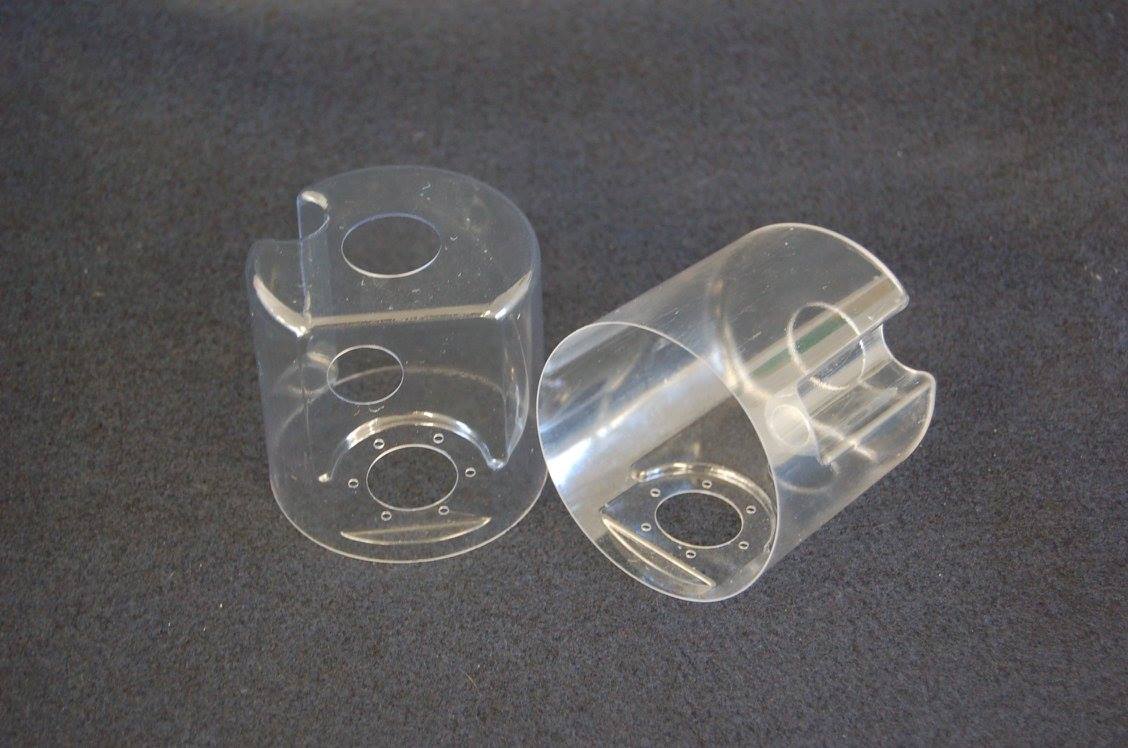

- Film is moved into position over the mold in either sheet form or roll form
- Film is clamped in place in a frame that holds the edges of the sheet
- Film is heated until softened
- Mold is introduced into the softened sheet and vacuum is applied
- Film is allowed to cool while still on the mold
- Formed sheet is removed from clamping frame
- Parts are rough trimmed from larger sheet
- Parts are final trimmed
- Inspect and Package
- Low tooling cost relative to injection molding
- Prototype speed (Prototype tools are typically less involved than with other methods)
- Parts with very small thickness to area ratios can be fabricated
- Extremely large parts can be fabricated
- High part cost relative to injection molded parts
- Non-uniform gauge due to film stretching
- Process is limited by geometry. Typically parts with undercuts are not achievable
Vacuum Forming: Term used to describe forming into a female mold
Drape Forming: Term used to describe forming over a male mold
Webbing: A phenomenon that occurs when the area of the melted sheet is larger than the mold’s ability to capture it. The result is excess film that folds onto itself creating “Webs”
Thermoforming window: The thermal range in which the particular polymer can be stretched and formed.
Select Male Mold when:
- Making tall parts
- Better part definition is required
- When you want thicker bottom (or top, if part is inverted) and thinner side walls
Select Female Mold when:
- Making shallow parts
- Side walls must be thicker and bottom thin
- Female mulitcavity tools fit more parts / unit area
- Definition is not required
High Performance Film Custom Manufacturing